About Internet Services
Internet services enable virtual machines (VMs) in a Net to be directly connected to the internet. Internet services can be used as target in route tables for network traffic directed to the internet.
An internet service is a component that you can attach to a Net to enable direct communication between your VMs in this Net and the internet. To do so:
-
You need to create a route in the route table of one or more Subnets directing internet traffic to the înternet service.
-
VMs in these Subnets must have a public IP associated with them.
-
You need to add appropriate rules allowing traffic to and from the internet to the security group of these Subnets.
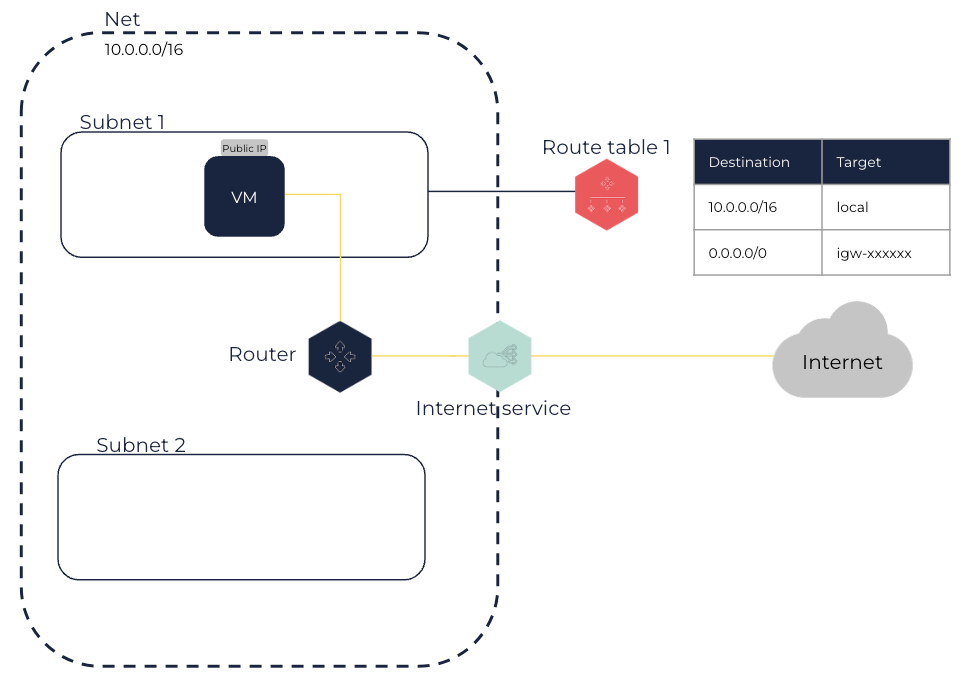
As VMs are only aware of the private IP space of the Net and Subnet, the internet service performs Network Address Translation (NAT) for your VMs using their public IP. When traffic leaves the Net Subnet to the internet, the internet service sets the reply address field to the public IP associated with the VM instead of the VM private IP. When traffic comes from the internet to a public IP associated with a VM, the internet service translates this public IP into the VM private IP before traffic reaches the Net, enabling it to reach the VM.
When creating a route to the internet service in the Subnet route table, you can use the 0.0.0.0/0 CIDR block as destination to scope all the destinations that are not explicitly routed in the route table, or you can use a smaller range of IPs corresponding, for example, to the public IPs of your internal network.
In a Net, the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is limited to 1500 bytes for packets directed to the internet using an internet service.
Related Pages