About Client Gateways
A client gateway is located on your side of a VPN connection, and manages traffic between your corporate network and your Net in the OUTSCALE Cloud.
Its counterpart on the OUTSCALE side of the VPN connection is a virtual gateway. For more information, see About Virtual Gateways and About VPN Connections.
General Information
A client gateway is the entry and exit point to your corporate network on your side of a VPN connection.
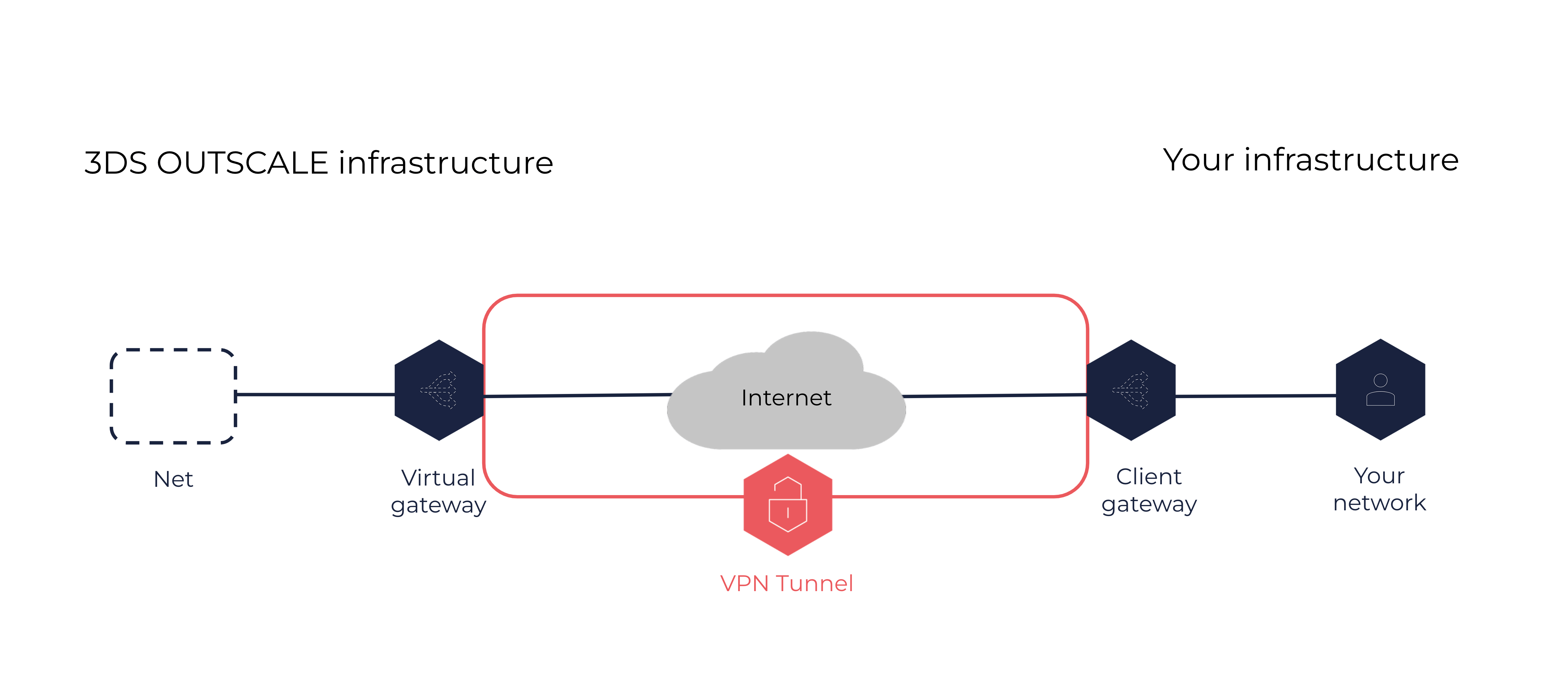
You identify an existing resource in your network to work as client gateway. It can be either software or hardware, for example a virtual machine (VM), a firewall, or a router. When creating a client gateway, you need to provide the following information:
-
The static public IP of the resource you want to use as client gateway.
-
The type of routing. To use dynamic routing, you need to provide a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Autonomous System Number (ASN). Otherwise, the routing is static. For more information, see About Routing Configuration for VPN Connections.
You can have several client gateways in the same corporate network at the same time. This enables you, for example, to connect your corporate network with several of your Nets in the OUTSCALE Cloud.
|
If you want to use different Nets simultaneously, you can create several client gateways with the same IP and a different ASN. |
Lifecycle
A client gateway can be in one of the following states:
-
Pending: The creation process is in progress.
-
Available: The client gateway is created and ready to use.
-
Deleting: The deletion process is in progress.
-
Deleted: The specified resource is no longer identified as a client gateway. However, the resource is not deleted.
Deleted resources remain visible for 1 hour.
Related Pages